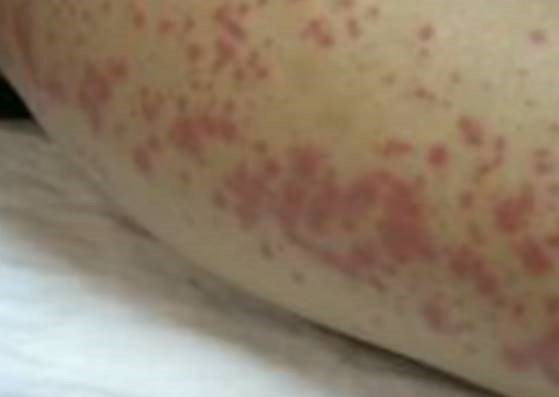
Leptospirosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria that can cause fatal infection of the kidney, liver, brain, lung or heart. Signs and symptoms can range from mild headaches, muscle pains, and fevers to severe bleeding in the lungs and a person to turning yellow from kidney failure. There are 13 different genetic types of leptospira that may cause disease in humans. Although disease cannot be spread from human to human, health providers have found that leptospirosis can be transmitted to humans by domestic animals. The leptospira germs that cause leptospirosis is carried in the urine of rats. If domestic animals, such as dogs, cats, cattle, pigs and horses are not properly managed the germs can get into their food source. Once a domestic animal becomes infected with leptospirosis the germ can easily be transmitted to us through contact. In many cases, problems develop around waste disposal or rather the lack of it, can lead to an increase in the population of rats, and so the suspected cases of leptospirosis will increase.